Living with a chronic digestive disorder can significantly impact your daily life, from managing symptoms to navigating dietary restrictions and emotional challenges. However, with the right coping strategies and a holistic approach to wellness, improving your quality of life and finding relief is possible.
Coping with these conditions requires a multifaceted approach that addresses physical, emotional, and dietary aspects. One avenue worth exploring on your journey toward better gut health is the use of gut health supplements. These supplements, formulated with specific nutrients and beneficial microorganisms, can support and optimize the functioning of your digestive system.
Understanding Chronic Digestive Disorders: An Overview of Common Conditions
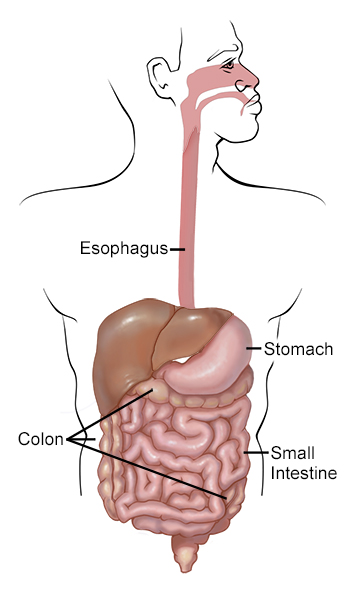
Chronic digestive disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the gastrointestinal system, causing persistent symptoms and disruptions to daily life. By gaining a deeper understanding of these conditions, individuals can better navigate their challenges and seek appropriate management strategies. Some common chronic digestive disorders include the following:
Crohn’s Disease
A chronic inflammatory bowel disease that ultimately leads to gastrointestinal tract inflammation and damage is Crohn’s disease. Crohn’s disease may have similarities with ulcerative colitis as both conditions lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, fatigue, and weight loss. However, ulcerative colitis only damages the innermost lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur on any part of the digestive system or bowel wall layers.
Celiac Disease
One of the digestive disorders which can be triggered simply by consuming gluten is Celiac disease. This autoimmune disorder damages the small intestine, causing a patient to experience digestive symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. Additionally, it can result in systemic manifestations, affecting other organs and systems in the body.
Irritable Colon
An irritable colon (i.e., IBS, mucus colitis) is characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits, often alternating between constipation and diarrhea. It is a functional disorder, meaning no structural abnormalities are detected, and its primary cause remains unclear. However, triggers such as stress, certain foods, and hormonal changes can exacerbate symptoms.
Gastritis
Gastritis refers to inflammation of the stomach lining, which can occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or persist over time (chronic gastritis). It can be caused by factors such as infection, excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or autoimmune disorders. Symptoms may include indigestion, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased inclination for food.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition characterized by the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. It occurs due to a weakened lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to escape into the esophagus.
Managing Symptoms: Coping Strategies for Pain, Discomfort, and Digestive Disturbances
Living with chronic digestive disorders often involves dealing with a range of symptoms, including pain, discomfort, and digestive disturbances. While the specific symptoms may vary depending on the condition, several coping strategies can help individuals effectively manage and alleviate their symptoms.
Understanding Your Symptoms
The first step in managing symptoms is to gain a clear understanding of what triggers them and how they manifest in your body. Keeping a symptom journal can be immensely helpful in identifying patterns and potential triggers. A more accurate diagnosis and targeted management strategies can be developed by tracking your symptoms, as well as any factors associated with their occurrence.
Diet and Nutrition
Dietary modifications often play a significant role in managing digestive symptoms. Identifying trigger foods and implementing an elimination diet can help determine which foods aggravate your symptoms. A registered dietitian can provide valuable guidance in developing a personalized meal plan that avoids trigger foods, incorporates gut-friendly choices, and ensures optimal nutrition.
Medication and Treatment Options
Depending on the specific condition and severity of symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend medications or other treatment options. It is essential to have open and honest communication with your healthcare team to discuss the available options, potential benefits, risks, and possible side effects of medications.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can have a profound impact on digestive symptoms, often exacerbating pain and discomfort. Engaging in stress reduction techniques can help manage symptoms effectively. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and progressive muscle relaxation can help relax the body and mind, promoting overall well-being and reducing digestive distress.
Pain Management Strategies
Chronic digestive disorders often involve varying degrees of pain. Exploring non-pharmacological pain management techniques can be beneficial. Applying heat therapy to the affected area, using hot water bottles or heating pads, can help alleviate pain and relax muscles. Relaxation exercises, such as guided imagery or gentle stretching, can also provide relief. It is important to discuss pain medication options with your healthcare provider, as they can prescribe appropriate pain relief medications if necessary.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Some individuals find relief from symptoms through alternative and complementary therapies. Acupuncture, herbal remedies, and probiotic supplementation are examples of therapies that some people incorporate into their treatment plans. However, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before trying these approaches to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your condition.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications can have a positive impact on managing symptoms. Prioritizing regular sleep patterns, practicing good sleep hygiene, and ensuring adequate hydration can support digestive health. Avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods, caffeine, alcohol, or smoking, can help reduce symptoms. Similarly, regular physical activity, such as low-impact exercises or walking, can aid digestion and alleviate discomfort.
Seeking Support
Dealing with chronic digestive disorders can be emotionally challenging. Building a support network and connecting with others who face similar challenges can provide a sense of understanding and validation.
Self-Care
Engaging in self-care activities is crucial for overall well-being and managing symptoms. Taking time for yourself, engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, practicing self-compassion, and setting realistic expectations can significantly improve your ability to cope with pain, discomfort, and digestive disturbances.
Take Charge of Your Gut Health with Proper Health Management Techniques
The gut plays a crucial role in our overall well-being, functioning as a complex ecosystem that influences various aspects of our health. Chronic digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, gastritis, and others can cause persistent discomfort, pain, and disruption to daily activities. The key to improving well-being is to understand and manage common conditions, manage symptoms, and implement coping strategies. Remember, it’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals and adopt a holistic approach that encompasses physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors. With the right knowledge, support, and proactive mindset, individuals can successfully cope with chronic digestive disorders and cultivate optimal gut health.