Synonym: Febrile Neutropenia
Definition of Neutropenic Fever
Fever:
- Single oral temperature ≥ 38.3 °c (101 °F) or
- ≥ 38 °c (100.4 °F) sustained over 1 hour
Neutropenia:
- Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) <500 cells/cu.mm or
- ANC expected to fall <500/cu.mm in next 48 hours
Profound neutropenia: ANC <100/cu.mm
Prolonged neutropenia: Neutropenia for >7 days
Risk Assessment in Neutropenic Fever
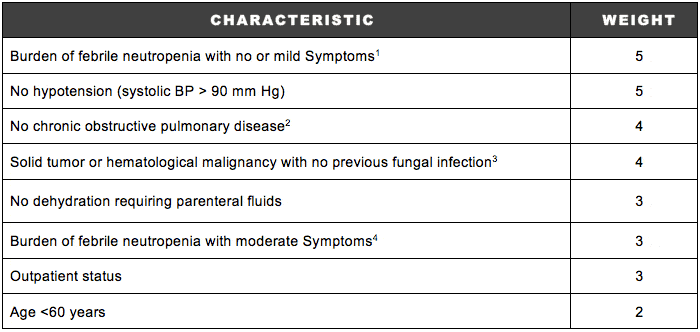
Multinational Association for Supportive Care in Cancer (MASCC) scoring system 1 :
High risk patients – Candidates for Inpatient and Parenteral therapy:
- MASCC score <21
- Anticipated prolonged and profound neutropenia
- Significant medical comorbidities – including hypotension, pneumonia, new-onset abdominal pain, or neurologic changes
Low risk patients – Candidates for Oral therapy:
- MASCC score ≥21
- Neutropenia not meeting criteria for ‘high risk’
- Few or no medical comorbidities
Laboratory Assessment in Neutropenic Fever
For all patients:
- CBC including DLC and platelets
- RFT – Serum creatinine and BUN
- Serum electrolytes
- LFT – AST/ALT, Total bilirubin
- Atleast 2 sets of blood cultures:
- If central venous catheter present: 1 set from each lumen of CV catheter and another from peripheral venous site
- If central venous catheter absent: 2 sets from separate venipuncture
If indicated clinically:
- Culture specimens from other sites
- Chest Xray
- Urinalysis
Oral Empiric Regimens for Low risk Neutropenic Fever
- Amoxicillin/Clavulanate + Ciprofloxacin
- If on fluoroquinolone prophylaxis – exclude oral fluoroquinolone from empiric therapy
- Other: Levofloxacin or Ciprofloxacin monotherapy, or Ciprofloxacin + Clindamycin (if penicillin allergic)
Empiric Regimens for High risk Neutropenic Fever
1st line Monotherapy: Antipseudomonal Beta-lactam agents
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam
- Cefepime
- Meropenem
- Imipenem-Cilastin
Fluoroquinolones, Aminoglycosides or Vancomycin may be added for management of complications or antimicrobial resistance.
Modification of initial empiric therapy:
- MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staph Aureus) – Early addition of vancomycin, daptomycin or linezolid
- VRE (Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus) – Early addition of daptomycin or linezolid
- ESBLs (Extended spectrum Beta Lactamase producing gram negative organisms) – Early use of Carbapenems
- KPCs (Klebsiella Pneumonia Carbapenemase) – Early use of polymyxin/colistin or tigecycline 2