Table of Contents
Among the common lysosomal storage disorders:
- Two of them are Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hunter and Hurler syndrome)
- Pompe’s disease is Glycogen Storage Disease.
- Others are Sphingolipidoses.
Inheritance of Lysosomal Storage Diseases
All are inherited as Autosomal Recessive (AR) condition except:
- Hunter syndrome (X-linked recessive)
- Fabry’s disease (X-linked recessive)
Higher risk in Ashkenazi Jews
Mnemonic: Ashkenazi Jews Drink TaNG
- Tay-Sach’s disease
- Niemann Pick’s disease
- Gaucher’s disease
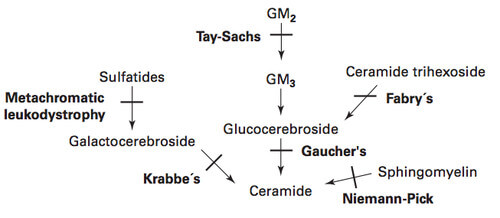
Enzyme Defects in Lysosomal Storage Diseases
I couldn’t create any mnemonics that could help me remember the enzymes involved in Lysosomal Storage Disease. I thought, best would be to memorize them:
| Lysosomal storage disorders | Enzyme deficiency | Accumulating substance |
| Tay-Sachs disease | Hexosaminidase A | GM2 ganglioside |
| Niemann-Pick disease | Sphingomyelinase | Sphingomyelin |
| Gaucher’s disease | Glucocerebrosidase | Glucocerebroside |
| Fabry disease | Alpha-Galactosidase A | Ceramide trihexoside |
| Metachromatic leukodystrophy | Arylsulfatase A | Sulfatides |
| Krabbe’s disease (Globoid cell leukodystrophy) | Beta-Galactocerebrosidase (Galactosylceramidase) | Galactocerebroside |
| Hurler syndrome (Type I MPS) | Alpha-L-iduronidase | Dermatan and Heparan sulfate |
| Hunter syndrome (Type II MPS) | Iduronosulfate sulfatase | Dermatan and Heparan sulfate |
Few mnemonics:
- HurLer syndrome: α-L-iduronidase
- HunTer syndrome: Iduronate sulfaTase
- Fabry’s disease: alpha-galactosidase A (Fabulous Alpha–Guy)
- Beta-galactosidase is deficient in GM1 gangliosidosis.
- Gaucher’s disease: Glucocerebrosidase (G for G)
- Niemann-Pick’s disease: Sphingomyelinase (Spi–N or No-Man Picks his nose with sPhinger)
- Metachromatic leukodystrophy: Arylsulfatase (Ar–Med)
- Krabbe’s disease: Beta-galactocerebrosidase
- Tay-Sach’s disease: Hexosaminidase A (taysaX lacks heXosaminidase A)
- Gaucher’s have “U” hence, lacks Glucocerebrosidase and Krabbe’s don’t have “U” hence, lacks Galactocerebrosidase.

Hurler vs Hunter Syndrome
The mode of inheritance and enzymes involved are different as mentioned earlier. Besides, other differences are:
- Hunter needs eyes to shoot: Hence, eyes are spared in Hunter syndrome while, corneal clouding is a feature of Hurler’s syndrome.
- Hunter’s are brainier: Mental retardation is seen in both but is more severe in Hurler syndrome.
- Gargoyle’s Hurl balls of fire: Gargoylism (Gargoyle facies is a feature of Hurler syndrome).
Hepatosplenomegaly is due to accumulation of dermatan and heparan sulfate and seen in both.
Other important facts:
- Mental retardation is absent in Morquio’s syndrome (MPS type IV).
- All mucopolysaccharidosis except San-fillipo syndrome cause growth retardation and short stature.
- Scheie is the mildest, Hurler-Scheie is intermeidate and Hurler syndrome is the severest form of MPS I.
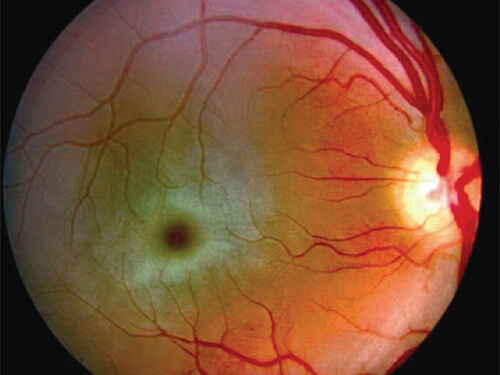
Cherry-Red Spots in Sphingolipidoses
- Tay-Sach’s Disease (GM2 gangliosidsosis type I)
- Niemann-Pick’s disease
- Metachromatic leukodystrophy
- Sandhoff disease (Globose accumulation due to lack of Hexosaminidase A and B preventing conversion of Globose into Ceramide trihexoside; GM2 gangliosidosis type II)
- Farber’s disease (not Fabry’s disease !!! – lack of Acid ceramidase intervening conversion of ceramide into Sphingosine)
- GM1 gangliosidosis (deficient beta-galactosidase blocking the conversion of GM1 ganglioside to GM2 ganglioside).
Mnemonic: Tay-Sach’s and Niemann-Pick’s both are hyphenated and have cherry red spots as feature.
Remember: Cherry red spots is not a feature of Fabry’s and Gaucher’s disease.
Hepatosplenomegaly in Sphingolipidoses
- Hepatosplenomegaly is present in those with cherry-red spots except: Tay-Sach’s disease and Metachromatic leukodystrophy
- Gaucher’s disease
Remember: Hepatosplenomegaly is not a feature of Tay-Sach’s disease and Fabry’s disease.
CNS involvement in Sphingolipidoses
CNS involvement is not a feature of Gaucher’s disease type I (most common form). However, type II and III do present with CNS involvement.
| Hepatosplenomegaly | CNS symptoms and Cherry red spot | ||
| + | – | ||
| + | Niemann-Pick’s | Gaucher’s | |
| – | Tay-Sach’s | Something else | |
Macrocephaly and Microcephaly
- Macrocephaly: Tay-Sach’s disease
- Microcephaly and Optic atrophy: Krabbe’s disease (Globoid cell leukodystrophy)
Fabry’s disease
Mnemonic: FABRy
Fabry’s disease cause:
- Angiokeratomas on skin and Acroparesthesis
- Blood vessel: Hypertensoin
- Renal failure
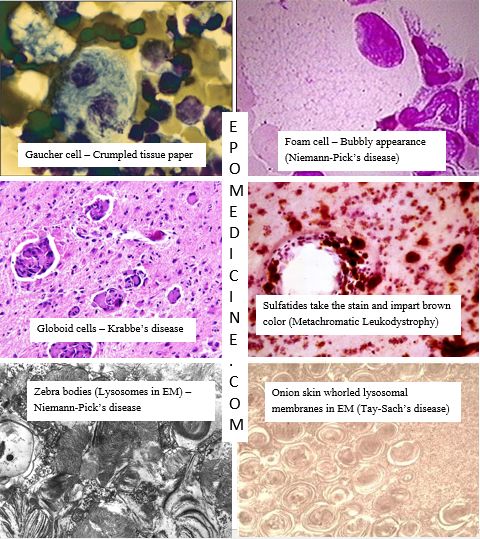
Cells in Sphingolipidoses
- Niemann-Pick’s disease: Zebra bodies (Distended lysosomes containing lamellated figures in Electron Microscopy), Foam cells/macrophages
- Gaucher’s disease: Gaucher cells/macrophages (crumpled tissue paper appearance)
- Tay-Sach’s disease: Onion-skin layers of whorled membrane within lysosomes (Electron microscopy)
- Krabbe’s disease (Globoid cell leukodystrophy): multinucleated Globoid cells
- Metachromic leukodystrophy: PAS + macrophages, Hirsh-Peiffer reaction (Sulfatides bind to cresyl violet and gives brown color instead of purple, i.e. metachromasia).

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music.

Thank you for this easy way to memorize this topic! I appreciate your work
Tnx…